Arthritis – 9 ways to reduce your risk or delay its onset
Arthritis is a common but often misunderstood condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It refers to a group of more than 100 different types of joint disorders that cause inflammation, pain, and stiffness. Although mainly associated with older people, arthritis can affect anyone, including those in their early 20s or even teenagers.
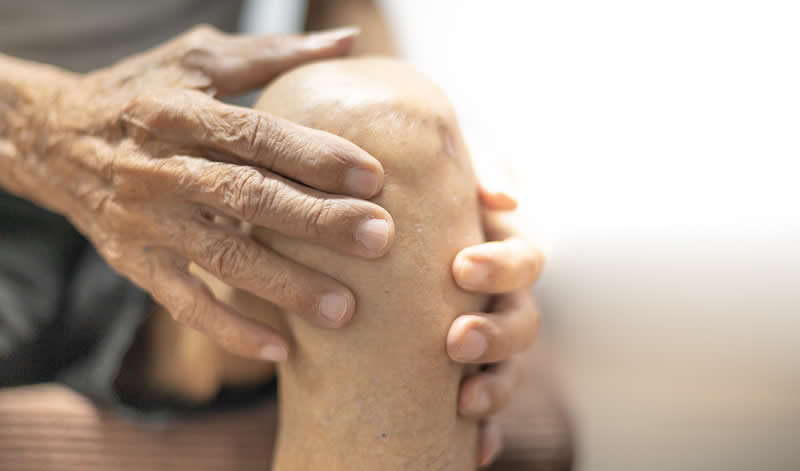
Early signs include stiffness and pain in the small joints of your hands and feet when you get up in the morning. You may find it painful to open a jar of coffee or fasten the buttons on clothing. However, the pain usually eases after an hour or so. That’s because physical activity helps loosen the joints, while inactivity makes the symptoms worse.
Over time, the condition may spread to the larger joints, such as the hips and knees. Arthritis in the fingers can lead to joint deformities, which significantly impact your quality of life.
What causes arthritis?
Arthritis can have various causes, depending on the type. The most common types of arthritis are:
- Osteoarthritis is usually associated with ageing, and results from wear and tear on the joints over time.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder, where the body’s immune system attacks the lining of the membranes that surround the joints.
- Gout – another form of arthritis – is caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints.
- Psoriatic arthritis affects those with the skin condition, psoriasis, which may spread to your joints.
Can arthritis be prevented?
While some factors like age and genetics are beyond your control, it is possible to reduce the risk or delay the onset of the disease by adopting a healthy lifestyle and making choices that promote joint health. Even if you can’t prevent it entirely, there are some steps you can take:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight – excess body weight puts additional stress on your joints, especially those in the knees, hips, and spine. Losing weight or maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce the risk of developing arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis.
- Stay Active – regular physical activity is crucial for joint health. Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, walking, and yoga help strengthen the muscles around your joints and improve joint flexibility.
- Protect Your Joints – avoid joint injuries by making sure you use proper techniques during physical activities. Wear appropriate footwear, and use joint support if necessary. If you find activities physically demanding, take regular breaks to rest your joints.
- Balanced Diet – adopt a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts. These foods have anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce inflammation associated with arthritis.
- Stay Hydrated – drinking plenty of water helps maintain the lubrication of your joints and supports overall joint health.
- Avoid Smoking –smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Quitting smoking not only reduces this risk but also has numerous other health benefits.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption – excessive alcohol consumption may increase the risk of gout, a form of arthritis caused by the build-up of uric acid in the joints.
- Manage Stress – high stress levels can contribute to inflammation in the body, potentially worsening arthritis symptoms. Use techniques such as meditation, mindfulness, and relaxation exercises.
9. Regular medical checkups: Early detection and treatment, particularly in the case of rheumatoid arthritis, can prevent or delay its progression.
What treatment is available?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are commonly used to manage symptoms and slow down disease progression.
In addition you may benefit from physical therapy, with an exercise plan specifically designed to improve joint function and reduce pain.
In severe cases, joint replacement surgery, such as knee or hip replacement, may be necessary to restore mobility and alleviate pain.
Understanding arthritis, its symptoms, causes, prevention strategies and treatment options, can help you manage the condition more effectively and improve your overall quality of life. If you suspect you have arthritis or are experiencing joint pain, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance.






 Look after your liver
Look after your liver Tee off at Tafta’s Golf Day Fundraiser
Tee off at Tafta’s Golf Day Fundraiser FullBright scholar arrives in June
FullBright scholar arrives in June Conversation Cards break communication barriers
Conversation Cards break communication barriers Secrets to longevity – what are they?
Secrets to longevity – what are they? Overcoming the ‘invisible woman’ syndrome
Overcoming the ‘invisible woman’ syndrome Saying it with flowers
Saying it with flowers Leap year – an extra ‘bonus’ day to show your love
Leap year – an extra ‘bonus’ day to show your love Save tax with Section 18A
Save tax with Section 18A Intergenerational communication is key
Intergenerational communication is key